Table of Contents
In a world where artificial intelligence is rapidly transforming industries from finance to healthcare, the kitchen is one of the newest frontiers. From smart ovens to recipe-generating algorithms, AI-created recipes are challenging the traditional role of chefs and pushing the boundaries of creativity, precision, and personalization in food. But can robots really cook better than chefs? Or is this high-tech trend simply a flashy gimmick?
In this article, we’ll delve deep into how AI-created recipes are developed, the rise of robot chefs, the advantages and limitations of AI cooking technology, and whether artificial intelligence in food can truly replace the intuition and soul of a human cook.
The Rise of AI in the Kitchen
Artificial intelligence is no longer confined to labs and coding environments—it has entered the kitchen. Companies like IBM, Google, and startups such as Plant Jammer, NotCo, and Chef Watson have already ventured into the culinary world. These platforms use machine learning to create new dishes by analyzing ingredients, taste profiles, and cooking techniques.
The concept of AI-created recipes is deceptively simple: feed data into an algorithm—ingredients, flavors, nutrition, and cooking styles—and let it generate original combinations. But under the hood, these AI systems are anything but simple. They rely on massive datasets, natural language processing (NLP), and neural networks to generate suggestions that are innovative, balanced, and tailored to specific dietary needs.
IBM’s Chef Watson, for example, uses cognitive computing to come up with novel culinary combinations. It pulls from chemical compound databases to suggest recipes that are both unexpected and sensorially harmonious. It has produced dishes like the Austrian Chocolate Burrito and Turmeric, Coconut, and Squid Ceviche, showcasing how AI-created recipes can push culinary boundaries in creative ways.
Robot Chefs in Action
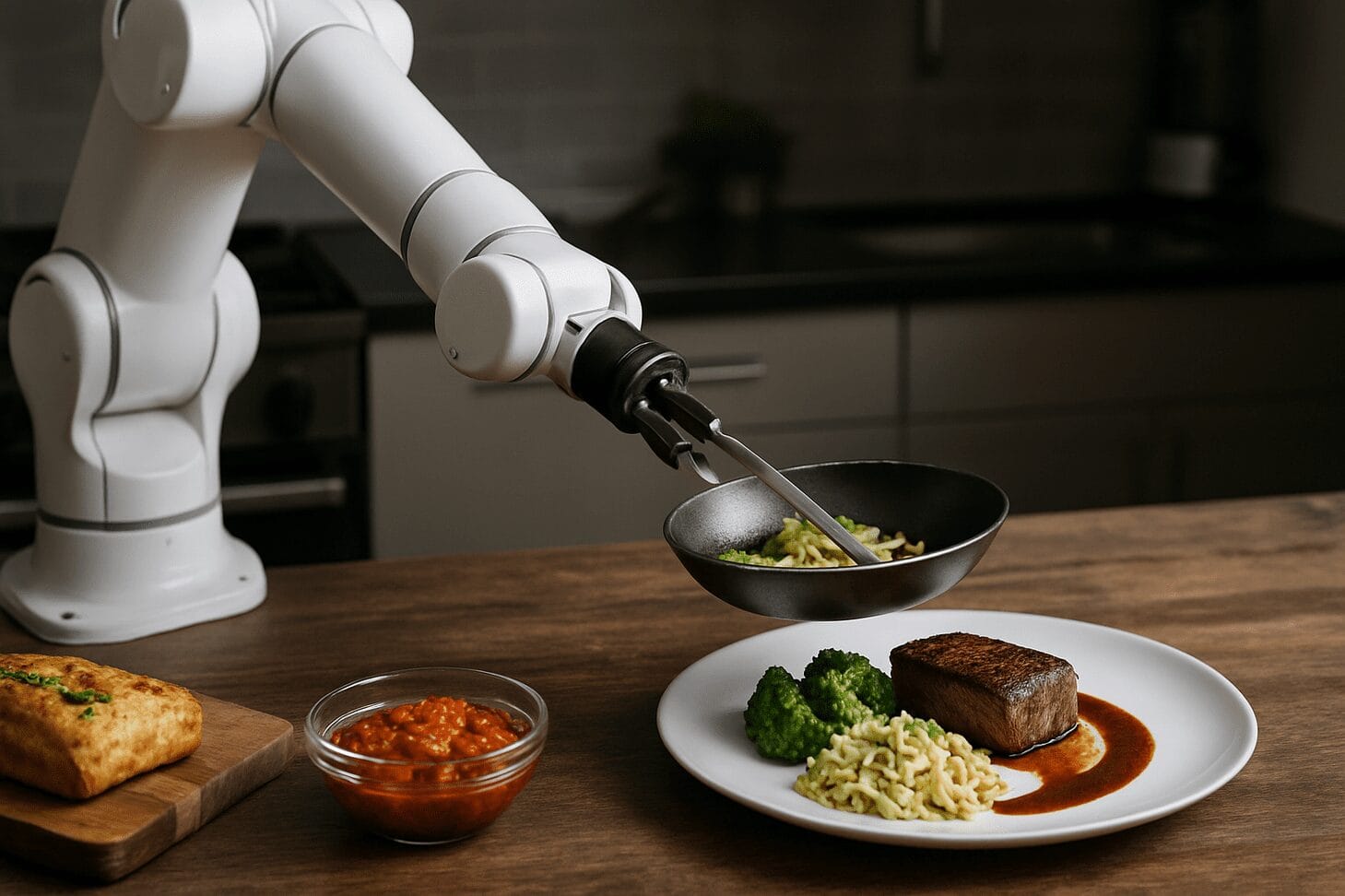
AI is not just about generating recipes—it’s also about executing them. Robot chefs are increasingly finding their place in both home and professional kitchens. Companies like Moley Robotics, Creator, and Miso Robotics have pioneered kitchen robotics capable of executing recipes from start to finish.
Moley’s robotic kitchen is a prime example. It features a fully automated cooking unit equipped with two robotic arms that can mimic the precise hand movements of a trained chef. These arms are programmed using motion capture technology and can stir, pour, chop, and even clean up after cooking. The system integrates with AI-created recipes, allowing users to select meals from a digital menu, and then watch as the robot prepares them autonomously.
In commercial kitchens, robots like Creator and Flippy are taking over repetitive, time-sensitive tasks. Creator’s burger-making robot assembles gourmet burgers from scratch, slicing buns, grilling patties, and layering ingredients with millimeter-level accuracy. Flippy, meanwhile, has been deployed in fast-food chains to fry items and flip burgers, maintaining consistent cooking times and hygiene standards.
How AI-Created Recipes Work
At the core of AI-created recipes lies a foundation of data—millions of recipes, ingredient lists, nutritional facts, and culinary traditions. These datasets are used to train AI models in understanding which combinations work and why.
Natural language processing helps AI systems comprehend the structure of recipes, recognizing steps, measurements, and techniques. Machine learning algorithms then identify patterns, such as which ingredients often appear together, how flavors interact, and what cooking methods suit specific textures or nutritional goals.
Some AI systems take this a step further by allowing user input. For example, users might enter available ingredients, dietary preferences (like vegan or keto), or time constraints. The AI then generates a recipe tailored to those variables. The system might even cross-reference seasonal produce or local availability to enhance practicality and sustainability.
AI-created recipes don’t just blend ingredients; they balance flavor profiles (sweet, sour, salty, bitter, umami), textures (crunchy, creamy, chewy), and preparation techniques. This computational creativity opens the door to culinary inventions that even seasoned chefs may not have imagined.
Advantages of AI Cooking Technology
1. Creativity Without Constraints
Human chefs are often influenced by cultural traditions, personal taste, and culinary dogma. AI, however, is unconstrained by such biases. It explores combinations based on chemical compatibility and data patterns, leading to unconventional yet successful pairings. AI-created recipes like beetroot-chocolate pasta or wasabi-coconut sorbet might sound odd but can delight the palate in unexpected ways.
2. Nutritional Precision
AI cooking technology excels at nutritional personalization. Whether you’re diabetic, gluten-intolerant, vegan, or on a low-FODMAP diet, AI can factor in all dietary restrictions and still generate diverse, appetizing recipes. It can calculate precise caloric values, macronutrient ratios, and even recommend portion sizes based on biometric data.
3. Consistency and Efficiency
Robot chefs powered by AI do not suffer from fatigue, mood swings, or distractions. They can reproduce a dish with identical results every time. In high-volume kitchens, such consistency is crucial. Automation also reduces prep time, speeds up service, and minimizes human error, which is invaluable for both fast food and fine dining.
4. Global Accessibility
With platforms offering AI-created recipes to users worldwide, gourmet-style cooking is no longer exclusive to professional chefs or high-end kitchens. Anyone with a smartphone or smart appliance can experiment with inventive, healthy meals tailored to their tastes and needs.
5. Sustainability
AI can be a powerful ally in promoting eco-friendly cooking. By analyzing what’s locally available, in-season, or nearing expiry, AI can suggest recipes that minimize waste. Some systems also analyze the environmental impact of ingredients, helping users make more sustainable choices.
Challenges and Limitations
1. Lack of Human Intuition
Despite all its strengths, AI lacks the sensory perception and intuitive judgment of human chefs. A robot cannot smell a caramelizing onion or feel when a dough has the perfect elasticity. These sensory cues are vital in fine cooking, and AI currently cannot replicate them.
2. Cultural Context
Food is deeply embedded in cultural identity and rituals. AI-created recipes might mash up ingredients from different cuisines without understanding their cultural significance. Such blind innovation risks producing dishes that are technically sound but culturally insensitive.
3. Hardware Complexity
Most robotic kitchens are costly and require significant space and maintenance. Moley’s system, for example, is priced well above what the average consumer or small restaurant can afford. Until prices drop and systems become more user-friendly, adoption will remain limited.
4. Creativity Plateau
AI can generate novel recipes by remixing known elements, but its creativity is ultimately derivative. Unlike human chefs, who can invent new cooking techniques or fuse culinary art with storytelling, AI operates within the limits of its training data.
The Chef’s Perspective: Threat or Tool?
Chefs around the world are divided on the rise of AI in the kitchen. While some view it as a threat to culinary artistry, others embrace it as a creative partner. Forward-thinking chefs see AI cooking technology as an augmentation tool that enhances their work rather than replacing it.
Instead of spending hours on repetitive tasks or data analysis, chefs can now delegate these to AI and focus on plating, storytelling, and the dining experience. AI-created recipes can act as brainstorming tools, suggesting combinations that spark new culinary explorations.
In Michelin-starred kitchens, AI is unlikely to replace human chefs anytime soon. But in industrial food production, airline catering, hospital kitchens, and school cafeterias, AI can offer enormous benefits by optimizing nutrition, speed, and cost.
Case Studies: AI in Culinary Practice
NotCo (Chile)
Using a proprietary AI called Giuseppe, NotCo identifies plant-based ingredients that mimic the molecular structure of animal products. Giuseppe has helped create successful products like NotMilk and NotBurger. These AI-created recipes not only replicate taste and texture but also align with environmental sustainability goals.
Plant Jammer (Denmark)
This app empowers users to cook with what they have. Enter your ingredients, and the AI recommends balanced, flavorful meals. The app uses a “food pairing wheel” derived from flavor science, making improvisational cooking less intimidating and more nutritious.
Creator (USA)
Creator’s burger-making robot is a marvel of engineering. It builds burgers from scratch in under five minutes, slicing tomatoes and buns fresh, grinding meat, and applying sauces precisely. These burgers are designed from AI-created recipes that optimize taste and layering.
Consumer Reactions: Curiosity, Skepticism, and Adoption
Consumers are approaching AI-created recipes with a mix of intrigue and caution. Food is deeply personal and emotional, and some diners resist the idea of a machine preparing their meals. Others, particularly younger and tech-savvy users, are eager to explore new culinary landscapes powered by AI.
Taste tests conducted with AI-generated dishes have often surprised participants with their originality and flavor harmony. In some cases, diners couldn’t tell whether a meal was prepared by a human chef or a machine. This growing acceptance suggests that AI may soon become a household culinary assistant.
However, trust remains a hurdle. Concerns about data privacy, recipe transparency, and food safety still need to be addressed before widespread adoption can occur.
The Future of Cooking: Collaboration Over Competition
Looking ahead, the most promising future lies in collaboration between chefs and AI. Rather than competing, AI and humans can co-create meals that are not only delicious but also personalized, nutritious, and sustainable.
In the future kitchen, a smart fridge may suggest meals based on what’s inside, while a robot preps the ingredients. The chef then finishes the dish with flair and intuition, creating a hybrid of automation and artistry.
Virtual reality, voice assistants, and even 3D food printing may integrate with AI to offer an immersive culinary experience. Cooking classes could evolve into AI-guided tutorials, and recipe books may be replaced by interactive digital platforms that adapt in real time.
Conclusion: Can Robots Cook Better Than Chefs?
So, can AI-created recipes and robot chefs truly outcook human chefs?
If “better” means faster, more consistent, and nutritionally precise, then yes, robots and AI cooking technology hold a clear advantage. But if “better” includes intuition, cultural storytelling, and artistic expression, then human chefs remain irreplaceable.
Ultimately, the real power of AI lies not in replacing chefs but in extending their capabilities. By handling the science, AI frees chefs to focus on the art. The future of cooking is not about man versus machine but about man with machine—a culinary symbiosis that promises to elevate food in ways we’ve only just begun to taste.
ore from The Daily Mesh:
- Esports in Schools: The New Varsity Sport?
- How AI is Being Used in Game Design
- The New Migration Routes of 2025: Causes and Consequences