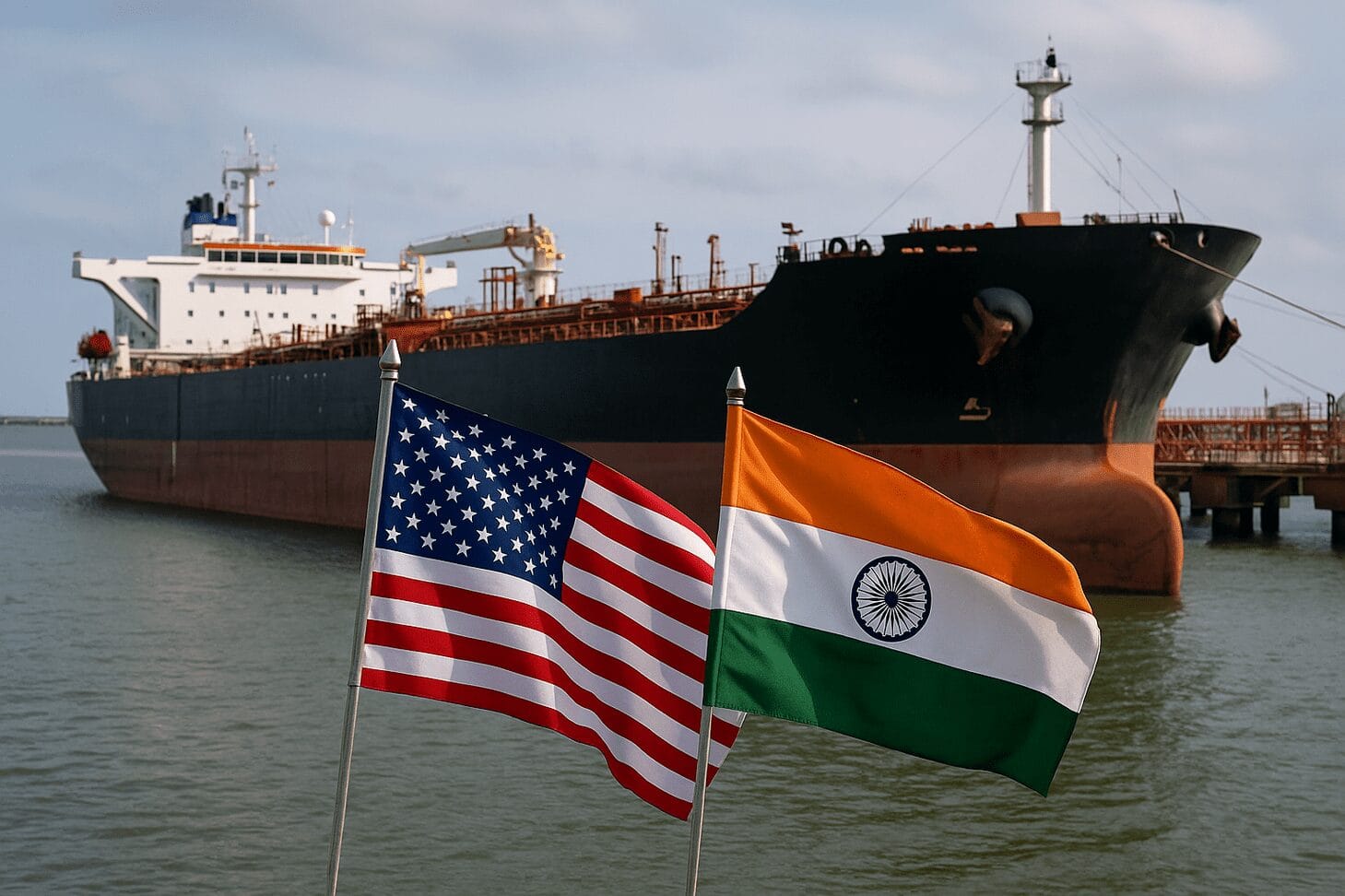
Introduction: A Widening Rift in a Strategic Partnership
In a year marked by turbulent geopolitical developments, one of the most quietly consequential stories continues to simmer between two major democracies — the United States and India. At the heart of this diplomatic rift lie US–India trade tensions stemming from India’s continued reliance on Russian oil imports, despite growing international sanctions and the West’s push to isolate Moscow economically.
While Washington views India’s strategic oil trade with Russia as a threat to its broader framework of geopolitical sanctions, New Delhi insists it is exercising sovereign rights to ensure energy security. The result is a growing divergence in bilateral trade relations, threatening to strain a strategic alliance crucial for counterbalancing Chinese influence in the Indo-Pacific region.
This article explores the evolution of these US–India trade tensions, assesses the economic and political stakes, and analyzes the implications for global trade, diplomacy, and energy policy.
Section 1: Background to the Tensions – How We Got Here
The Rise of Russian Oil Imports
Following Russia’s 2022 invasion of Ukraine, Western nations — led by the US and the European Union — imposed severe sanctions on Russia, particularly targeting its lucrative fossil fuel exports. While the EU rapidly cut its reliance on Russian oil, other nations, especially India and China, seized the opportunity to purchase discounted crude from Moscow.
India’s Russian oil imports skyrocketed, rising from less than 1% of its total crude intake in early 2022 to over 40% by mid-2025. This shift not only diversified India’s energy sources but also provided significant cost savings — critical for a nation with ballooning energy demands and rising inflation.
US Position and Expectations
Washington, while initially tolerant due to India’s non-alignment and energy dependency, began increasing pressure as the war in Ukraine continued. US officials have urged India to gradually reduce oil trade with Russia, arguing that continued purchases undermine the effectiveness of the geopolitical sanctions designed to cripple the Kremlin’s war machine.
However, India has maintained that its energy policies are guided by national interests. Indian External Affairs Minister Dr. S. Jaishankar famously responded in 2023, “Europe buying Russian gas is not funding the war, but India buying oil is?”
This divergence has since deepened the US–India trade tensions.
Section 2: Strategic Stakes and Domestic Pressures
India’s Energy Security vs. Political Optics
India’s decision to maintain, and even deepen, its oil relationship with Russia is rooted in realpolitik. With over 1.4 billion people and an economy growing at 6–7% annually, India’s energy security is not a luxury — it is a necessity.
At the same time, the Modi administration is preparing for national elections in 2026, and managing fuel prices is politically sensitive. Cutting off Russian oil would either require more expensive alternatives or result in domestic shortages — both of which could damage the incumbent government.
American Political Constraints
Meanwhile, the Biden administration faces its own domestic challenges. With mounting criticism over the handling of the Ukraine conflict and a charged political environment ahead of the 2026 midterm elections, Washington cannot afford to appear weak on sanctions enforcement.
Additionally, Congress has seen increasing bipartisan calls for a tougher stance on nations “aiding Russia’s war economy.” India, despite being a strategic partner, is not exempt from scrutiny.
This confluence of domestic pressures has turned a quiet disagreement into a public contest, intensifying US–India trade tensions.
Section 3: Diplomatic Dialogues and Breakdown Points
High-Level Talks and Mutual Frustration
Throughout 2024 and early 2025, diplomatic efforts to bridge the divide were frequent but inconclusive. Meetings between Indian and US trade representatives highlighted the gap in priorities.
The US offered access to discounted US LNG (liquefied natural gas) and strategic reserves if India agreed to a gradual wind-down of Russian oil imports. India, however, cited logistical and pricing issues and declined.
Behind closed doors, sources indicated that both nations had grown increasingly frustrated — India by what it sees as moral posturing, and the US by India’s hedging strategy.
G20 Fallout
At the 2025 G20 summit in Rio de Janeiro, the rift became more visible. In side discussions on energy security and supply chain resilience, India blocked a clause that would have formally condemned oil purchases from sanctioned nations. Analysts viewed this as a direct rebuke to Washington’s stance and a symbolic assertion of India’s independent foreign policy.
Section 4: Economic Impacts of US–India Trade Tensions
Slowing Bilateral Trade Growth
According to the US Department of Commerce, trade between the two nations grew by only 3.5% in the first half of 2025 — a significant slowdown from the 8.7% annual growth seen in previous years. US exports to India have been particularly affected, with aerospace, defense, and semiconductor deals seeing delays or stagnation.
India’s own trade strategy appears to be shifting toward new partnerships in the BRICS+ framework, especially with Brazil, South Africa, and the UAE.
Technology and Tariff Retaliation Risks
While no formal sanctions or tariffs have been imposed yet, both sides have exchanged regulatory jabs. The US recently reclassified some Indian tech imports as “strategic-sensitive,” requiring extra licensing, which India sees as protectionism.
Indian lawmakers are also mulling retaliatory tariffs on US agricultural exports if pressure over Russian oil escalates. Such moves could impact billions in bilateral trade and aggravate already fragile bilateral trade relations.
Section 5: Broader Geopolitical Implications
Indo-Pacific Strategy and the China Factor
One of the key concerns in Washington is that alienating India could inadvertently push it closer to China — or at least toward a more neutral posture in the evolving Indo-Pacific balance of power. While India is unlikely to align directly with Beijing, it could reduce its cooperation in the Quad (Quadrilateral Security Dialogue), which includes the US, Japan, and Australia.
Washington’s aggressive stance on Russian oil imports risks complicating what was until recently a rising strategic partnership aimed at deterring Chinese assertiveness in the region.
Erosion of Trust and Strategic Autonomy
For India, the tension highlights a long-standing concern: dependence on any single geopolitical bloc, whether Western or Eastern, can threaten its autonomy. The country has reaffirmed its commitment to “strategic autonomy,” a Cold War-era doctrine emphasizing non-alignment.
If the current US–India trade tensions continue, it could have a chilling effect on broader military and technological cooperation between the two nations.
Section 6: The Russian Factor — What’s in it for Moscow?
Moscow, for its part, is reaping major benefits from the discord. India has become a lifeline for the Russian economy, buying oil, paying in rupees, and investing in joint refineries and port infrastructure in the Far East.
Russia has also used the tensions as diplomatic leverage, portraying itself as a dependable energy partner to the Global South, in contrast to what it describes as the “hypocritical” West.
As long as India continues to prioritize energy security, Moscow will have an incentive to support and deepen that relationship — complicating US goals further.
Section 7: Public Opinion and the Business Community
Indian Public Sees Pragmatism Over Pressure
In India, public sentiment largely supports the government’s stand. Many view US criticism as double standards, especially given that European countries continued buying Russian gas for much longer than India bought oil.
Indian business leaders argue that maintaining Russian oil imports is not just about cost but also about resilience and diversification.
US Industry Caught in the Crossfire
American companies, especially those in the tech, defense, and agriculture sectors, have expressed concern that escalating US–India trade tensions may harm long-term partnerships. Many have urged Washington to pursue dialogue over confrontation.
In an open letter, a coalition of over 80 US CEOs urged both governments to resolve differences and focus on “constructive engagement that strengthens the Indo-American economic corridor.”
Section 8: Potential Pathways to De-Escalation
Quiet Diplomacy and Strategic Concessions
Analysts suggest that a viable off-ramp could include backchannel diplomacy, where India agrees to cap Russian oil imports at current levels in exchange for enhanced US energy cooperation.
The US might also consider relaxing some export controls on critical tech transfers, helping India accelerate its energy transition while preserving strategic alignment.
Multilateral Forums and Global Mediation
Organizations like the International Energy Agency (IEA) and G20 could serve as platforms for compromise. A global oil pricing pact or a neutral mediation mechanism could allow both countries to save face while pursuing national interests.
Ultimately, resolving US–India trade tensions requires recognizing the legitimacy of each other’s positions — and acknowledging the complex intersection of energy, security, and diplomacy.
Conclusion: The Tensions Are Real — But So Are the Stakes
The growing strain over Russian oil imports has pushed US–India trade tensions into uncharted waters. While neither side wants a full-blown trade conflict, the friction is eroding trust at a time when strategic unity is paramount.
With elections looming in both countries and global energy markets in flux, the choices made in the next few months will reverberate well beyond oil. Whether the world’s oldest and largest democracies can find common ground — or let short-term pressures upend long-term partnerships — remains to be seen.
What is certain, however, is that these US–India trade tensions are not just about barrels of oil. They are about the architecture of a new global order in which power, principle, and pragmatism collide.
More from The Daily Mesh:
- AI-Created Recipes: Can Robots Cook Better Than Chefs?
- Coffee Trends in 2025: Beyond Espresso
- Street Food Goes Gourmet: Top Spots Around the World